
HOW DOES A FREEZER WORK?
Freezers help you preserve fresh foods and stock up on frozen favorites so you can serve them when you’re ready. Use this guide to learn how freezers keep food cold, discover different types of freezers and learn the best freezer settings for optimal performance.
WHAT IS A FREEZER?
Freezers preserve food by storing it at or below 0°F (-18°C). These appliances include large chest and upright deep freezers as well as refrigerator freezer combinations like top-freezer, side-by-side, French door and bottom-freezer models.
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE FREEZER
Refrigerators became a common household fixture in the late 1920s, but refrigerators with a separate, sizable freezer compartment didn’t become popular until the 1940s. Freezer compartments were originally only large enough to fit ice cube trays, but today’s domestic freezers can offer as much as 21 cubic feet of capacity.
PARTS OF A FREEZER
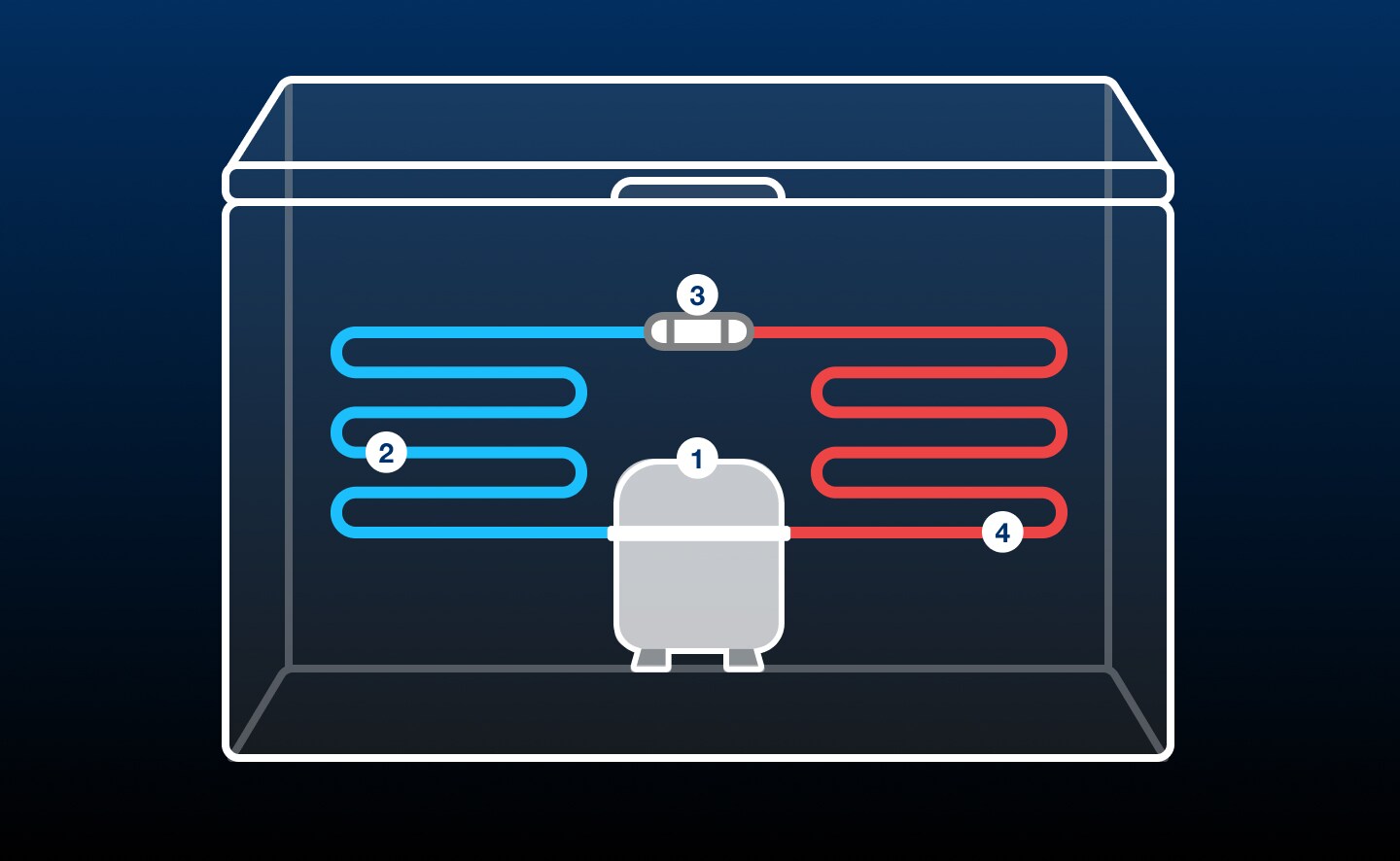
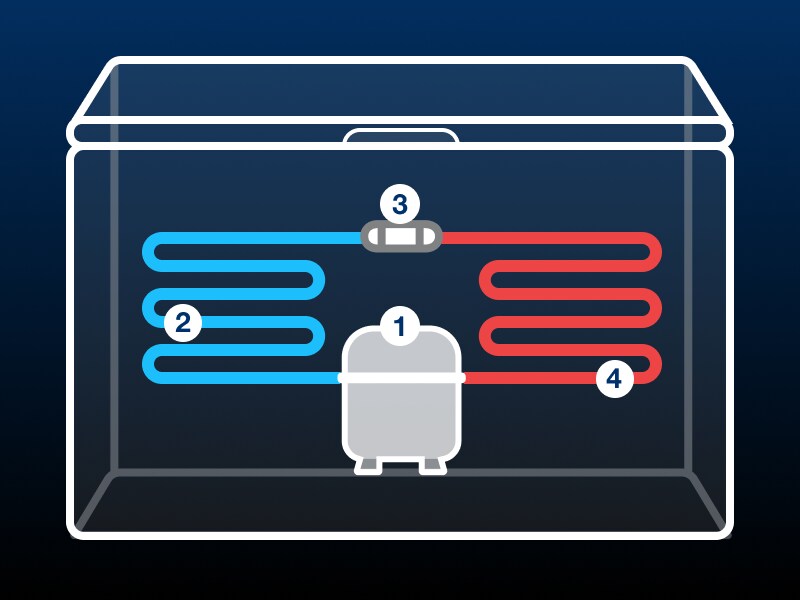
Freezers operate with the help of four main components, including the compressor, condenser coils, capillary tube and evaporator. Each of these components transports and chemically alters the refrigerant that ultimately absorbs and expels heat from the freezer cavity.
HOW DOES A FREEZER WORK?
A freezer moves refrigerant through its main components, expanding and contracting the substance as it travels to absorb and expel heat from the compartment. Discover the four main steps of the cooling process below.
STEP 1: COMPRESSOR PREPARES REFRIGERANT
Your refrigerator’s compressor kicks off the cooling cycle by drawing refrigerant vapor in, then it kicks up the heat to raise both the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant.
STEP 2: CONDENSER COILS LIQUIFY REFRIGERANT
The compressor pushes high-pressure refrigerant into the condenser coils where it undergoes a chemical transformation into a liquid.
STEP 3: CAPILLARY TUBE VAPORIZES REFRIGERANT
Liquified refrigerant makes its way from the condenser coils into the capillary tube where it undergoes a dramatic decrease in pressure. This pressure decrease causes the refrigerant to cool significantly in preparation to enter the evaporator, converting it back into a vapor.
STEP 4: EVAPORATOR & REFRIGERANT ABSORB HEAT
Finally ready to move heat out of the freezer cavity, the refrigerant enters its final phase in the cooling cycle as it moves through the evaporator to absorb heat from the inside of the freezer. Heat is expelled through the evaporator and the refrigerant returns to the compressor to start the cycle again.
HOW DIFFERENT FREEZERS WORK
From varying configurations to distinct feature sets, different freezer types offer unique benefits. Learn more about different types of freezers and what they have to offer below.
DEEP FREEZER
Deep freezers and fridge freezers both store food at or below 0°F (-18°C), but deep freezers only feature a freezer compartment which typically has a far greater storage capacity than refrigerator freezer compartments. Spanning anywhere from 5 cu. ft. to over 21 cu. ft. capacity, deep freezers are available in chest or upright configurations with plenty of storage space for bulky items.
CHEST FREEZER
Chest freezers are a type of deep freezer featuring a lid that opens upward on a horizontally oriented freezer compartment. Chest freezers like these models from Maytag brand typically feature a wide-open freezer compartment with a small number of baskets for organizing frozen items, making them ideal for large and bulky frozen items that require a flexible storage space.
fridge freezer
Refrigerator freezers are dual appliance units that feature both a refrigerator and freezer compartment in one. These types of freezers are typically found in four common configurations, including top-freezer, bottom-freezer, side-by-side and French door refrigerator models. Side-by-side refrigerator freezers usually offer a bit more freezer space than other configurations.
frost freezer
Frost freezers require manual defrosting when the ice on its walls measures at least ¼-inch thick. Many of today’s freezers are frost-free and automatically monitor and defrost the freezer’s interior as ice builds up. Though manual defrosting can be time-consuming, frost freezers may cost less to operate.
portable freezer
Portable freezers are compact freezer units that are small enough to move from location to location. These freezers plug into a power source and are reliable alternatives to traditional coolers for activities like tailgating or camping.


WHAT ARE COMMON USES OF THE FREEZER?
Freezers can help you stock up on your favorite fresh or frozen items, preserving them in their current state until you’re ready to serve them. You can prepare and freeze ingredients and meals to use later or take advantage of freezer capacity to shop in bulk or stock up during sales on your family’s most-used items.
HOW DO YOU AVOID FROST IN YOUR FREEZER
Opening your freezer door allows moisture to enter the compartment that ultimately transforms into frost on your freezer walls. Keeping your freezer properly defrosted can help prevent build-up that blocks air vents and temperature sensors, making it easier for your appliance to do its job.
If your freezer doesn’t include an auto-defrost option, be sure to manually defrost the freezer at least once a year to help it function properly. You can defrost your freezer by unplugging the unit and transferring food to a cooler. Then open the door and allow the ice to melt onto various towels placed below and inside of the freezer compartment. Clean out and dry the freezer once the ice is melted, then plug it back in and allow it to cool to freezing temperatures before replacing food.
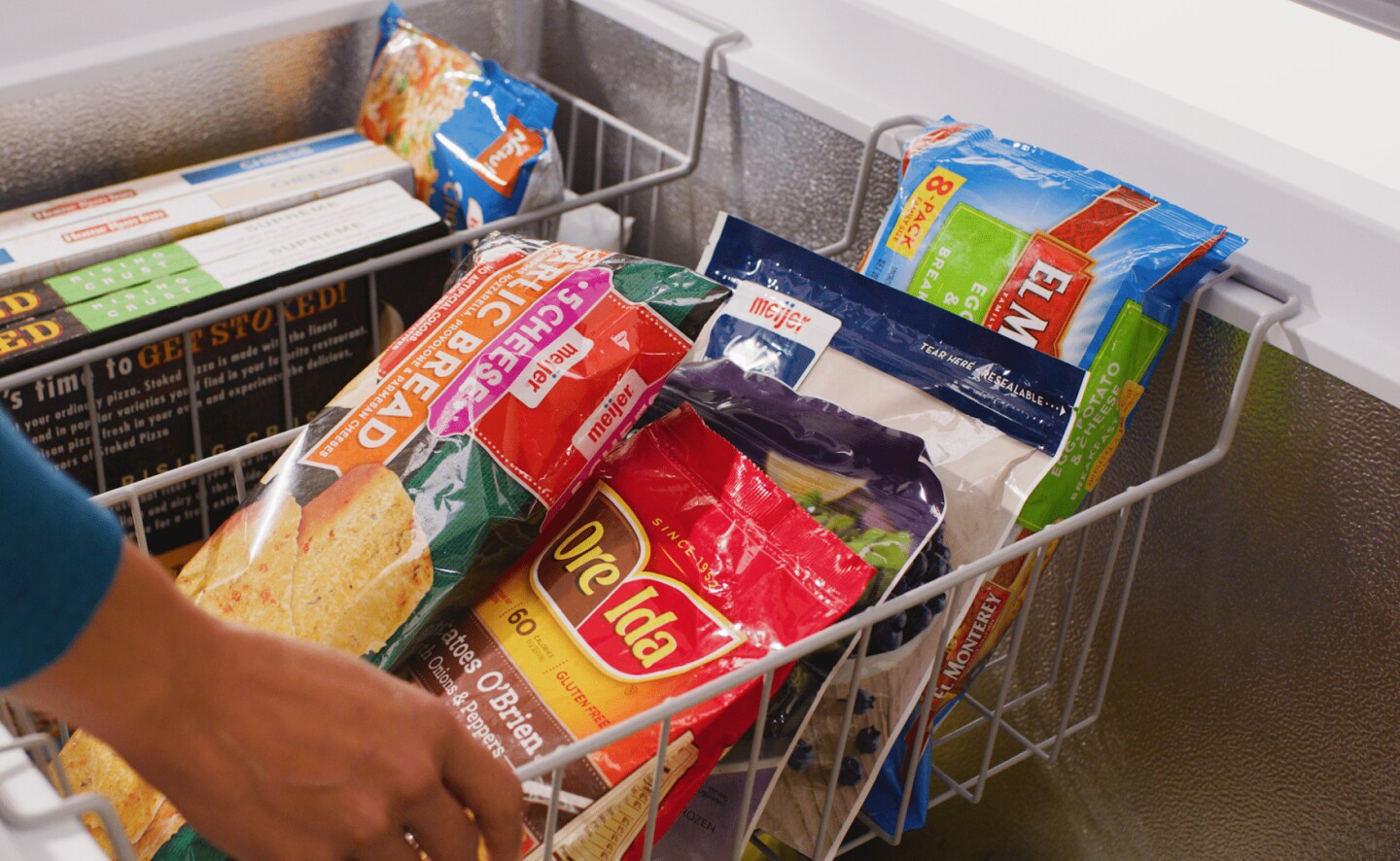


CAN YOU OVER-FREEZE FOOD?
A freezer on its coldest setting won’t ruin most foods, but food can only last so long in the freezer before it begins losing its intended texture and taste. Each type of food is different, but vegetables typically last anywhere from 8–12 months in the freezer, while most fruits last somewhere from 9–12 months. Uncooked beef, pork or poultry usually lasts up to a year, and fully cooked meats should stay fresh for 1–2 months.
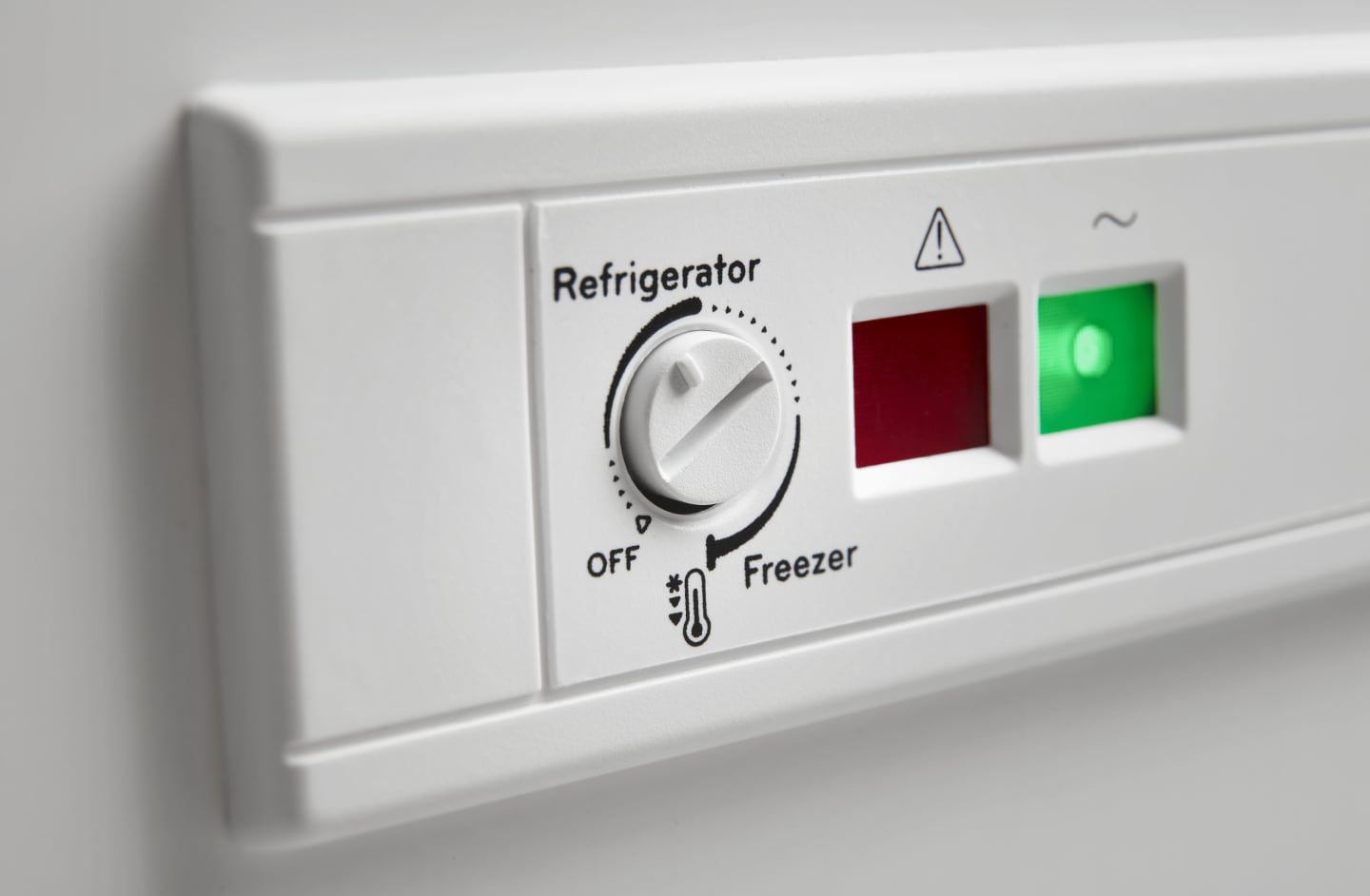


WHAT’S THE RIGHT SETTING FOR YOUR FREEZER?
Setting your freezer to 0ºF (-18ºC) can help your freezer and the food inside last as long as possible. Frost build-up on your freezer walls may mean the freezer temperature is set too low, while ice cream that’s easy to scoop may indicate that your freezer temperature is slightly too high. Remember that freezing foods that are still hot can cause temperature fluctuations in the freezer, so be sure to cool all foods completely before freezing.
SHOP ALL MAYTAG® FREEZERS
Maytag® chest and upright freezers keep food frozen around the clock so you can stock up on your favorite items, big or small. The FastFreeze option on select models drops the freezer to its coldest temperature for 24 hours to help seal in freshness after a big grocery trip. Plus, select models are garage ready, so they can withstand both hot and cold external conditions while keeping your food at just the right temperature.


